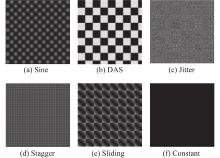
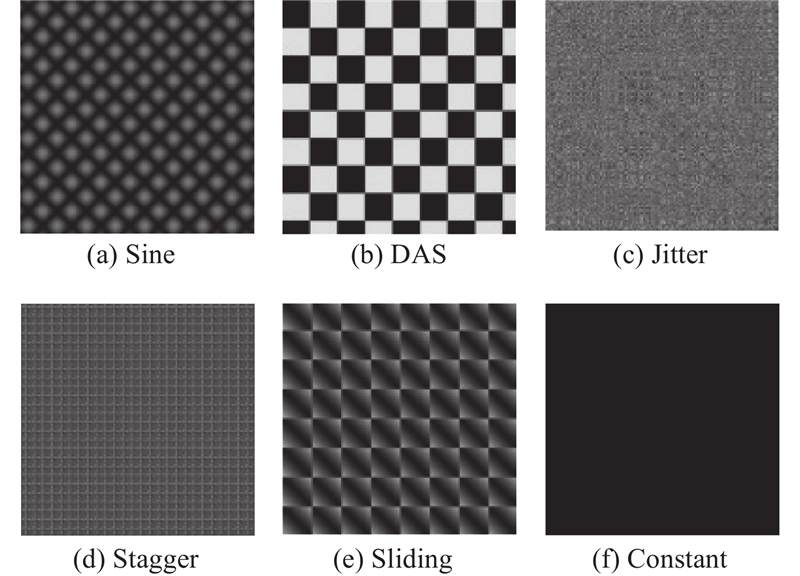
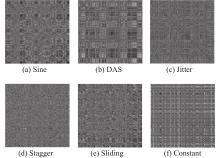
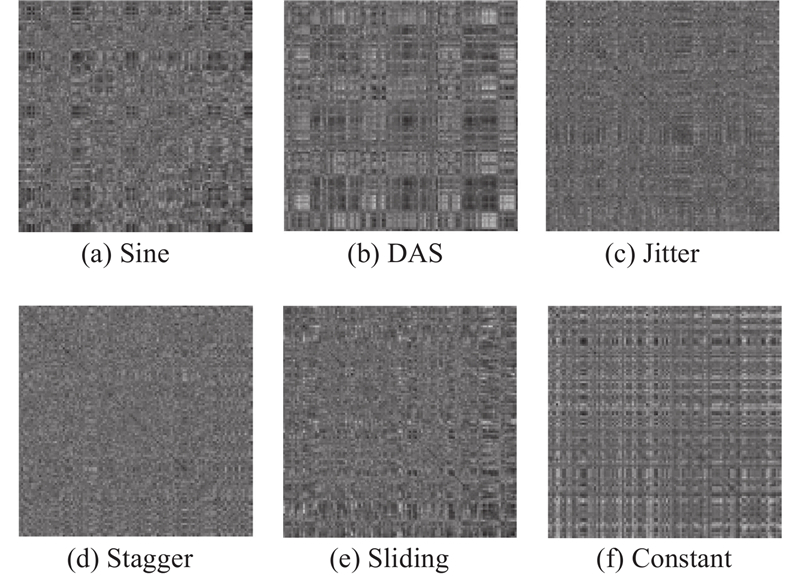
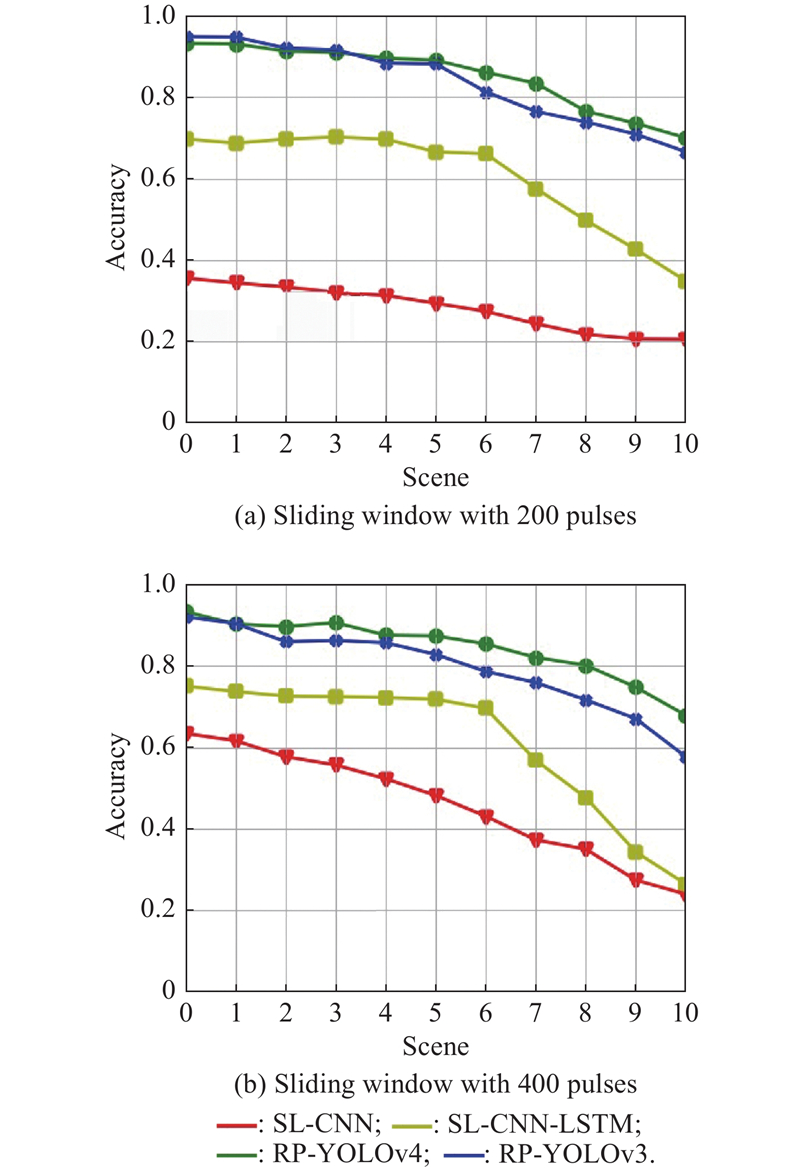
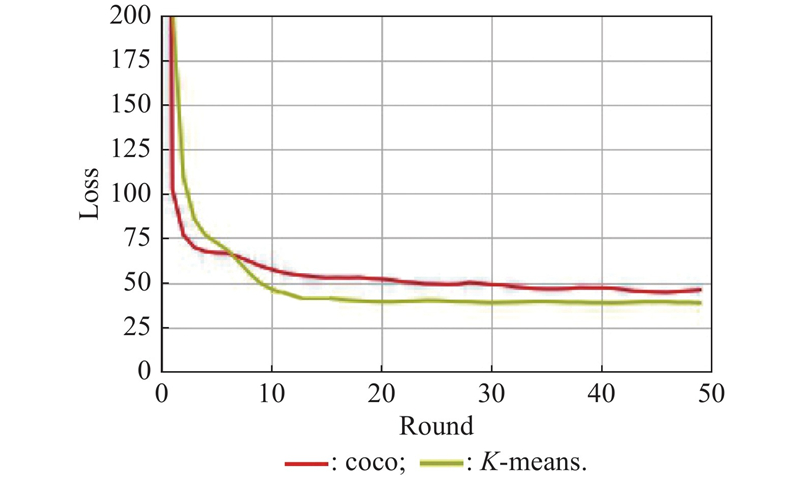
| 1 |
NISHIGUCHI K, KOBAYASHI M Improved algorithm for estimating pulse repetition intervals. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2000, 36 (2): 407- 421.
doi: 10.1109/7.845217
|
| 2 |
GENCOL K, KARA A, AT N Improvements on deinterleaving of radar pulses in dynamically varying signal environments. Digital Signal Processing, 2017, 69, 86- 93.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2017.06.010
|
| 3 |
GENCOL K, AT N, KARA A A wavelet-based feature set for recognizing pulse repetition interval modulation patterns. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences, 2016, 24 (4): 3078- 3090.
|
| 4 |
KAUPPI J P, MARTIKAINEN K, RUOTSALAINEN U Hierarchical classification of dynamically varying radar pulse repetition interval modulation patterns. Neural Networks, 2010, 23 (10): 1226- 1237.
doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2010.06.008
|
| 5 |
SHI R, WU C Review on technology research about radar pulse signal deinterleaving based on PRI information. Telecommunication Engineering, 2020, 60 (1): 112- 120.
|
| 6 |
TORUN O, KOCAMIS M B, ABACI H, et al Deinterleaving of radar signals with stagger PRI and dwell-switch PRI types. Proc. of the IEEE 25th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference, 2017, 1- 4.
|
| 7 |
HASANI H, KHOSRAVI M R Pulse deinterleaving based on fusing PDWs and PRI extraction process for radar-assisted edge devices considering computational costs. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2021, (1): 1- 14.
|
| 8 |
GUAN Y F, ZHANG G Y A radar emitter recognition method based on the PRI switching rules. Fire Control and Command Control, 2015, 40 (3): 79- 82.
|
| 9 |
LIU Z M Recognition of multifunction radars via hierarchically mining and exploiting pulse group patterns. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56 (6): 4659- 4672.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2999163
|
| 10 |
RICHARD G, WILEY E. The interception and analysis of radar signals. Boston: Artech House, 2006.
|
| 11 |
RAY P S A novel pulse TOA analysis technique for radar identification. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34 (3): 716- 721.
doi: 10.1109/7.705881
|
| 12 |
WANG J P, CHU C Q Approach to radar pulse repetition intervals modulation recognition based on Bayesian networks. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2007, 22 (2): 14- 17.
|
| 13 |
TAO R H, LI H S A novel algorithm of radar signal recognition based on histogram and wavelet networks. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2005, 20 (6): 784- 788.
|
| 14 |
KAUPPI J P, MARTIKAINEN K S An efficient set of features for pulse repetition interval modulation recognition. Proc. of the IET International Conference on Radar Systems, 2007.
|
| 15 |
MAHDAVI A, PEZESHK A M A robust method for PRI modulation recognition. Proc. of the IEEE 10th International Conference on Signal Processing, 2010, 1873- 1876.
|
| 16 |
LIU Y C, ZHANG Q Y An improved algorithm for PRI modulation recognition. Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, 2017.
|
| 17 |
LI X Q, HUANG Z T, WANG F H, et al Toward convolutional neural networks on pulse repetition interval modulation recognition. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22 (11): 2286- 2289.
doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2864725
|
| 18 |
NUHOĞLU M A Classification of radar signal features in electronic warfare with convolutional long-short time memory. Proc. of the IEEE 26th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference, 2018.
|
| 19 |
ZHANG J Y, SU S Y A method for the modulation pattern recognition of radar PRI based on fully convolutional neural network. Electronic Warfare Technology, 2020, 35 (3): 40- 45.
|
| 20 |
LI X, LIU Z, HUANG Z T Attention-based radar PRI modulation recognition with recurrent neural networks. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 57426- 57436.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2982654
|
| 21 |
WEI S Q, QU Q Z, WU Y T, et al PRI modulation recognition based on squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24 (5): 1047- 1051.
doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2970397
|
| 22 |
ECKMANN J P, KAMPHORST S O, RUELLE D Recurrence plots of dynamical systems. World Scientific Series on Nonlinear Science Series A, 1995, 16, 441- 446.
|
| 23 |
ZOLOTOVA N V, PONYAVIN D I Phase asynchrony of the north-south sunspot activity. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2006, 449 (1): L1- L4.
|
| 24 |
MARWAN N, TRAUTH M H, VUILLE M, et al Comparing modern and Pleistocene ENSO-like influences in NW Argentina using nonlinear time series analysis methods. Climate Dynamics, 2003, 21 (3/4): 317- 326.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-003-0335-3
|
| 25 |
NICHOLS J M, TRICKEY S T, SEAVER M Damage detection using multivariate recurrence quantification analysis. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2006, 20 (2): 421- 437.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2004.08.007
|
| 26 |
REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al You only look once: unified, real-time object detection. Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016, 779- 788.
|
| 27 |
REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger. Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 7263−7271.
|
| 28 |
REDMON J, FARHADI A. Yolov3: an incremental improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018.
|
| 29 |
BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M. Yolov4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020.
|
| 30 |
LI H, DENG L B, YANG C, et al Enhanced YOLO v3 tiny network for real-time ship detection from visual image. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 16692- 16706.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3053956
|
| 31 |
XU Q W, LIN R Z, YUE H, et al Research on small target detection in driving scenarios based on improved yolo network. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 27574- 27583.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2966328
|
| 32 |
CHEN H P, HE Z T, SHI B W, et al Research on recognition method of electrical components based on YOLO V3. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 157818- 157829.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2950053
|
 ), Weisong LIU(
), Weisong LIU( ), Zheng LIU(
), Zheng LIU( )
)